Cataracts are a common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the natural lens, leading to blurred vision and visual impairment. While cataracts are primarily associated with aging, they can also result from injury, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions. The impact of cataract treatment on vision can vary, and in some cases, individuals may experience significant vision loss.
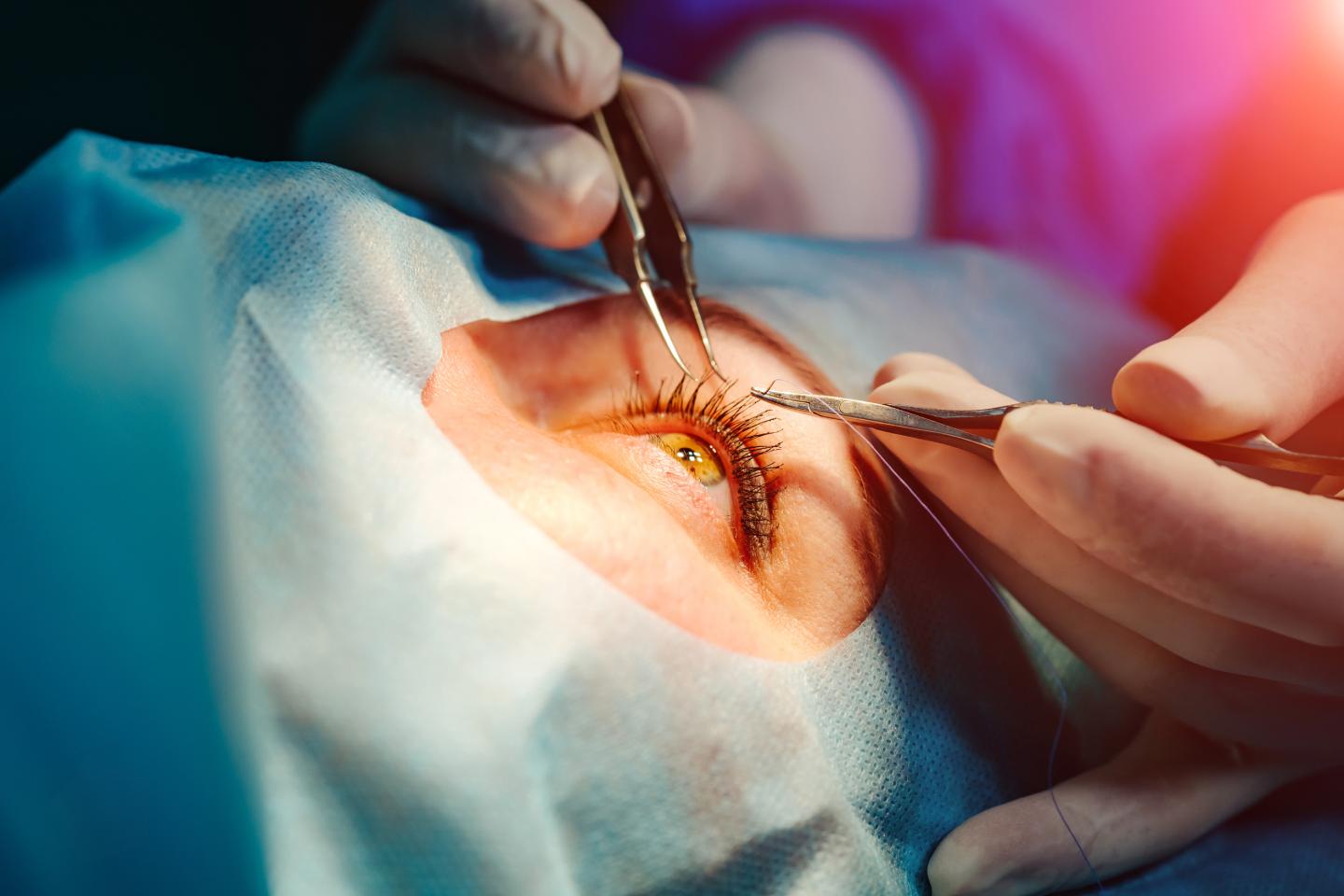
Cataract surgery is a highly effective and routine procedure that involves removing the cloudy lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). This surgery aims to restore clarity to the vision affected by cataract treatment. The success of cataract surgery in improving vision largely depends on various factors, including the individual’s overall eye health, the severity of the cataract, and any existing eye conditions.
In many cases, cataract surgery results in a remarkable improvement in vision. Patients often report clearer and sharper vision following the procedure, allowing them to resume daily activities with increased ease. However, claiming complete restoration of vision for every individual may be an oversimplification.
While cataract surgery can significantly enhance vision, achieving complete restoration may be influenced by several factors. One such factor is the presence of other eye conditions or diseases that may coexist with cataracts. Conditions like macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy can impact vision independently of cataracts, and addressing the cataract alone may not address these underlying issues.
Moreover, the health of the optic nerve and the retina plays a crucial role in determining the success of vision improvement after cataract surgery. If these structures are compromised due to other eye diseases or conditions, achieving complete vision restoration may be challenging.
It’s important to note that individual responses to cataract surgery can vary. While many individuals experience a significant improvement in vision, some may still require glasses for certain activities, particularly reading or driving. Factors such as pre-existing refractive errors or astigmatism may contribute to the need for glasses post-surgery.
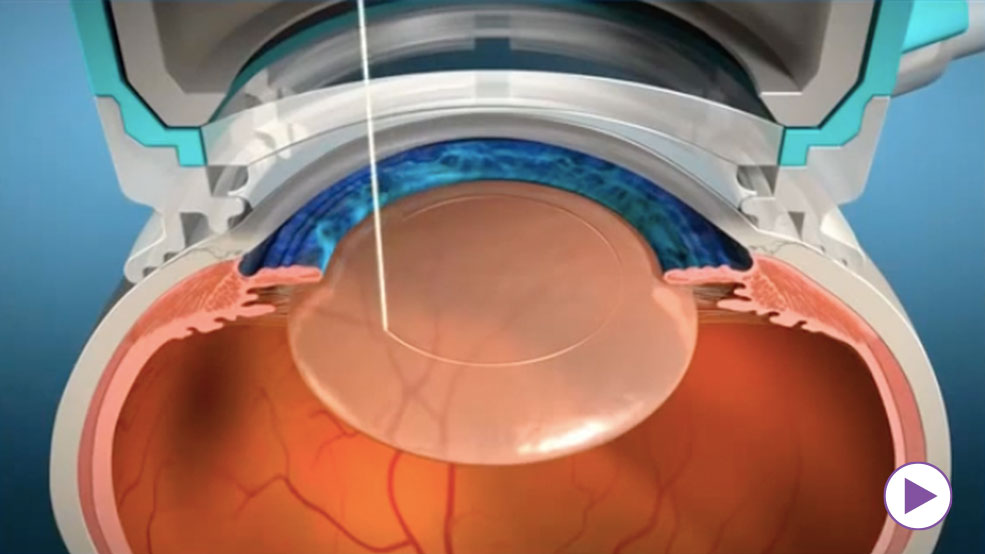
Advancements in cataract surgery techniques and technology continue to enhance outcomes. Laser-assisted cataract surgery, for example, offers a high level of precision, potentially leading to improved visual results. Additionally, the development of advanced intraocular lens options, including multifocal and toric lenses, aims to address specific vision needs and reduce dependence on glasses.
Cataract surgery is a highly successful and widely performed procedure that can significantly improve vision affected by cataracts. While complete restoration of vision is often achieved for many individuals, it’s essential to consider factors such as coexisting eye conditions and overall eye health. Consulting with an ophthalmologist can provide a personalized assessment of the potential outcomes of cataract surgery and help manage expectations regarding vision improvement.